Introduction
Project data is stored in JSON files.
An up-to-date detailed JSON file format description, directly generated from latest source code, is available on this website.
JSON evolution
The JSON format evolves as the app is updated and gains more functionalities. You can track these changes easily:
- List of JSON changes
- List of breaking changes (deprecations): if you write your own JSON importer, you should really pay attention to this part. It’s pretty easy to follow and it will save you some future debugging time.
- Learn more about deprecation cycles
Project JSON (*.ldtk)
This JSON file contains:
- project settings,
- all definitions,
- depending on the “Separate level files” option:
- if Separation is disabled: all level data, including layer content.
- if Separation is enabled: all level data, except layer content.
Example
Below is a simplified example of a typical empty LDtk project file:
{
"__header__": { // Some header information
"fileType": "LDtk Project JSON",
"app": "LDtk",
},
"iid": "9bba3440-7820-11ed-bc60-dd3cf5379687",
"jsonVersion": "1.2.2",
"worldLayout": "Gridvania",
"defs": { // Definitions of this project elements
"layers": [],
"entities": [],
"tilesets": [],
"enums": [],
"externalEnums": [],
"levelFields": []
},
"levels": [ // Actual level data
{
"identifier": "MyLevel0",
"iid": "472e4691-66b0-11ec-aa49-8d5f985d2dae",
"worldX": 0,
"worldY": 0,
"layerInstances": [], // Layers content
}
]
}Format overview
The file is mainly divided between 4 major blocks, but 2 are really important: definitions (defs) and level data (levels).
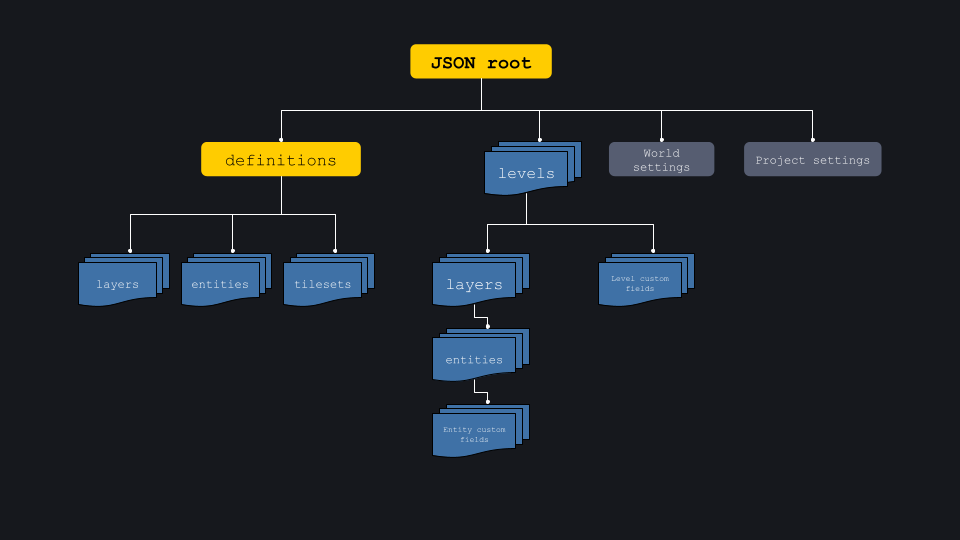
JSON root
Information stored in root
Most of these are only used by the editor itself.
File identification: __header
You probably don’t need this part as it only contains some information to identify the file itself (app, origin, human readable description etc.).
Definitions: defs
“Definitions” contain all the details and settings of each component in the project:
- layers,
- entities and their fields,
- tilesets,
- enums.
All level instances: levels
Level data contain the actual instances of each levels and their layers content, entities instances etc.